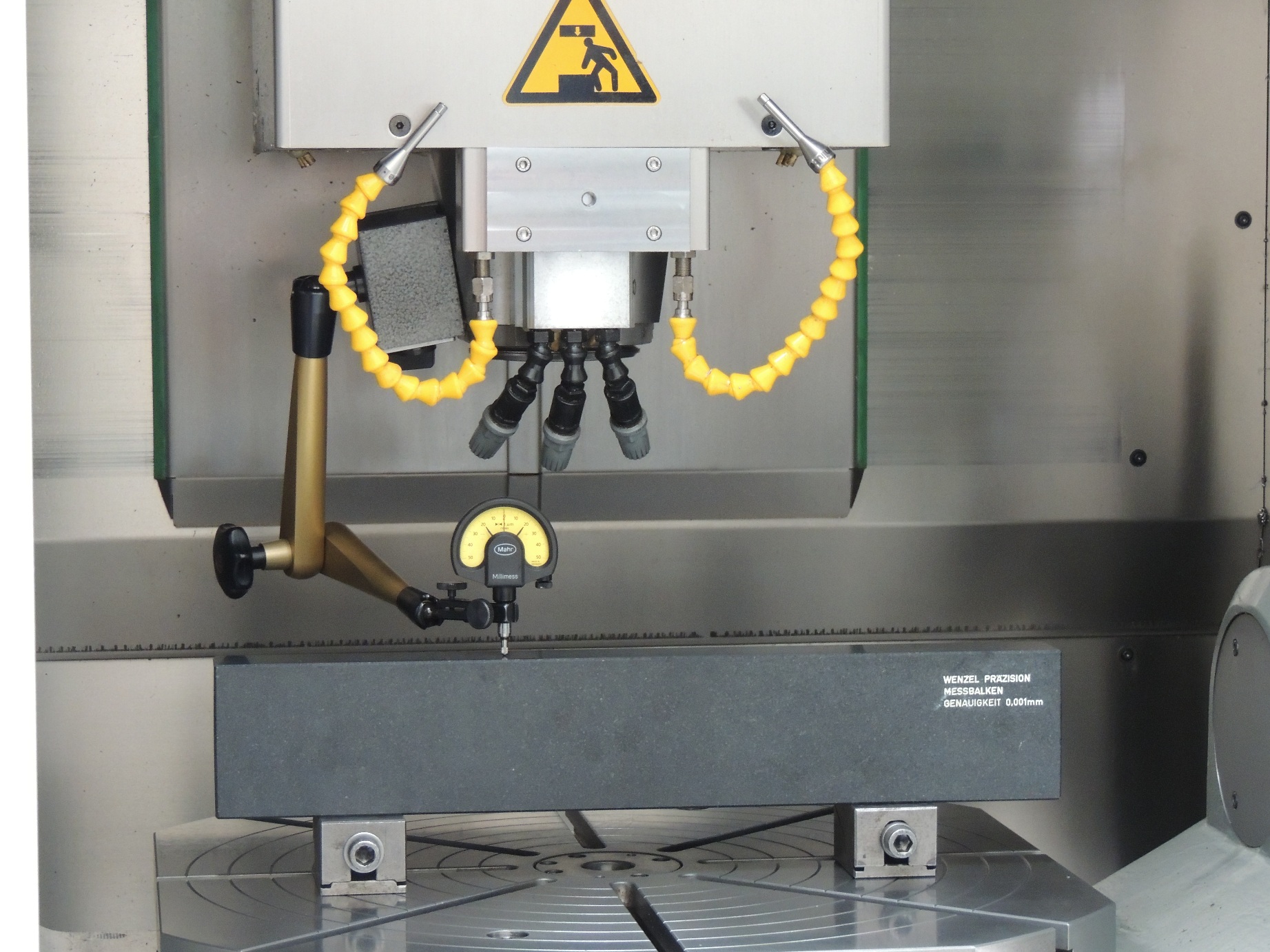

Geometric deviations have an direct effect on the workpiece accuracy. Included in the established acceptance guidelines are terms such as: straightness, squareness, parallelism, axial and concentricity, flatness and angular deviations - pitching, rolling and yawing.
Using modern measuring technology, we measure your machines and, if necessary, organize everything from realignment to retrofitting.

Geometric deviations have an direct effect on the workpiece accuracy. Included in the established acceptance guidelines are terms such as: straightness, squareness, parallelism, axial and concentricity, flatness and angular deviations - pitching, rolling and yawing.
Using modern measuring technology, we measure your machines and, if necessary, organize everything from realignment to retrofitting.
Geometric deviations have an direct effect on the workpiece accuracy. Included in the established acceptance guidelines are terms such as: straightness, squareness, parallelism, axial and concentricity, flatness and angular deviations - pitching, rolling and yawing.
Using modern measuring technology, we measure your machines and, if necessary, organize everything from realignment to retrofitting.
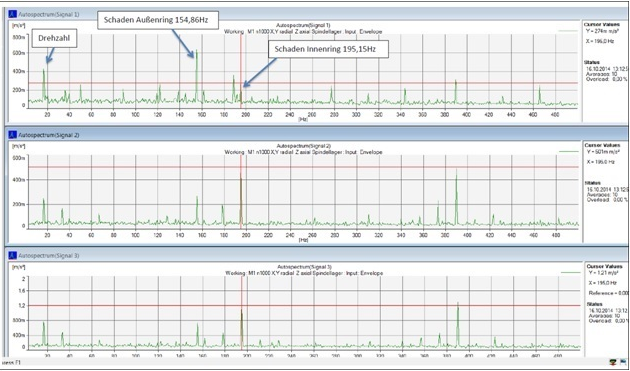
Vibration analysis is a method for identifying damaged machine components. Vibrations of moving parts such as bearings, shafts or gears are measured and evaluated. The results are used both for error prevention and error identification on machines. Necessary repair and maintenance work can be detected early and planned accordingly. The big advantage: Machine downtimes due to costly disassembly for visual inspection are eliminated.
Required is the knowledge of the installed machine components (documentation of the manufacturer).With this information characteristic damage frequencies can be calculated and compared with the occurring vibrations.
For example, you can detect well:
A method in which the condition of e.g. Bearings, gearings, guides, screw drives, etc. are recorded and documented at regular intervals, are referred to as Condition Monitoring. With this tool of modern maintenance, trend curves are generated from the measured data, which give a prognosis about the condition of the machine components.
Customers thus have a high degree of planning security as they always know the condition of their machines and plants.
If there is a problem with a production machine (noise, bad machining result, vibration, etc.), a simple and quick diagnosis by the machine operator or the maintenance personnel is often not easily possible. A time-consuming and expensive search with visual inspections, selective disassembly of components and exclusion procedures are the "approaches" to the problem.
ABS-Ingenieurdienstleistung GmbH saves customers the "try-and-error" principle.

Vibration analysis is a method for identifying damaged machine components. Vibrations of moving parts such as bearings, shafts or gears are measured and evaluated. The results are used both for error prevention and error identification on machines. Necessary repair and maintenance work can be detected early and planned accordingly. The big advantage: Machine downtimes due to costly disassembly for visual inspection are eliminated.
Required is the knowledge of the installed machine components (documentation of the manufacturer).With this information characteristic damage frequencies can be calculated and compared with the occurring vibrations.
For example, you can detect well:
A method in which the condition of e.g. Bearings, gearings, guides, screw drives, etc. are recorded and documented at regular intervals, are referred to as Condition Monitoring. With this tool of modern maintenance, trend curves are generated from the measured data, which give a prognosis about the condition of the machine components.
Customers thus have a high degree of planning security as they always know the condition of their machines and plants.
If there is a problem with a production machine (noise, bad machining result, vibration, etc.), a simple and quick diagnosis by the machine operator or the maintenance personnel is often not easily possible. A time-consuming and expensive search with visual inspections, selective disassembly of components and exclusion procedures are the "approaches" to the problem.
ABS-Ingenieurdienstleistung GmbH saves customers the "try-and-error" principle.
Vibration analysis is a method for identifying damaged machine components. Vibrations of moving parts such as bearings, shafts or gears are measured and evaluated. The results are used both for error prevention and error identification on machines. Necessary repair and maintenance work can be detected early and planned accordingly. The big advantage: Machine downtimes due to costly disassembly for visual inspection are eliminated.
Required is the knowledge of the installed machine components (documentation of the manufacturer).With this information characteristic damage frequencies can be calculated and compared with the occurring vibrations.
For example, you can detect well:
A method in which the condition of e.g. Bearings, gearings, guides, screw drives, etc. are recorded and documented at regular intervals, are referred to as Condition Monitoring. With this tool of modern maintenance, trend curves are generated from the measured data, which give a prognosis about the condition of the machine components.
Customers thus have a high degree of planning security as they always know the condition of their machines and plants.
If there is a problem with a production machine (noise, bad machining result, vibration, etc.), a simple and quick diagnosis by the machine operator or the maintenance personnel is often not easily possible. A time-consuming and expensive search with visual inspections, selective disassembly of components and exclusion procedures are the "approaches" to the problem.
ABS-Ingenieurdienstleistung GmbH saves customers the "try-and-error" principle.
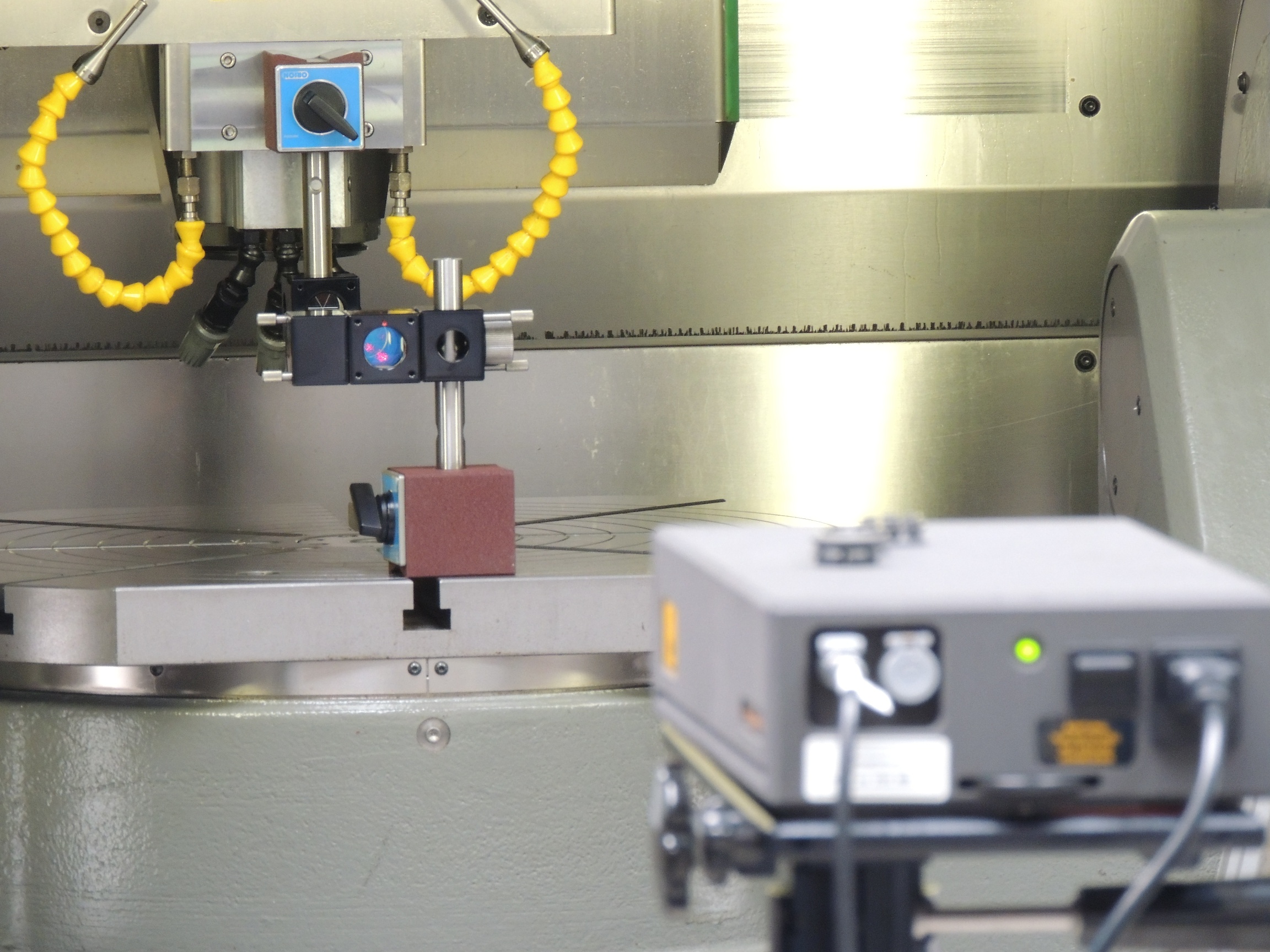
The position accuracy is a measurement how exact a certain position is approached. There are a variety of measuring and evaluation methods for determining the characteristic values - the most common methods are ISO230-2 and VDI3441.
We measure with a laser interferometer of Renishaw® and compensate for residual errors in the machine controller. By using a weather station, environmental influences such as changes in air temperature, pressure and humidity can be reduced to a minimum.
Whether final inspection, calibration after exchange of measuring system or in the course of routine machine inspection. Laser Interferometry - the fast and accurate way to calibrate your machine axes.

The position accuracy is a measurement how exact a certain position is approached. There are a variety of measuring and evaluation methods for determining the characteristic values - the most common methods are ISO230-2 and VDI3441.
We measure with a laser interferometer of Renishaw® and compensate for residual errors in the machine controller. By using a weather station, environmental influences such as changes in air temperature, pressure and humidity can be reduced to a minimum.
Whether final inspection, calibration after exchange of measuring system or in the course of routine machine inspection. Laser Interferometry - the fast and accurate way to calibrate your machine axes.
The position accuracy is a measurement how exact a certain position is approached. There are a variety of measuring and evaluation methods for determining the characteristic values - the most common methods are ISO230-2 and VDI3441.
We measure with a laser interferometer of Renishaw® and compensate for residual errors in the machine controller. By using a weather station, environmental influences such as changes in air temperature, pressure and humidity can be reduced to a minimum.
Whether final inspection, calibration after exchange of measuring system or in the course of routine machine inspection. Laser Interferometry - the fast and accurate way to calibrate your machine axes.
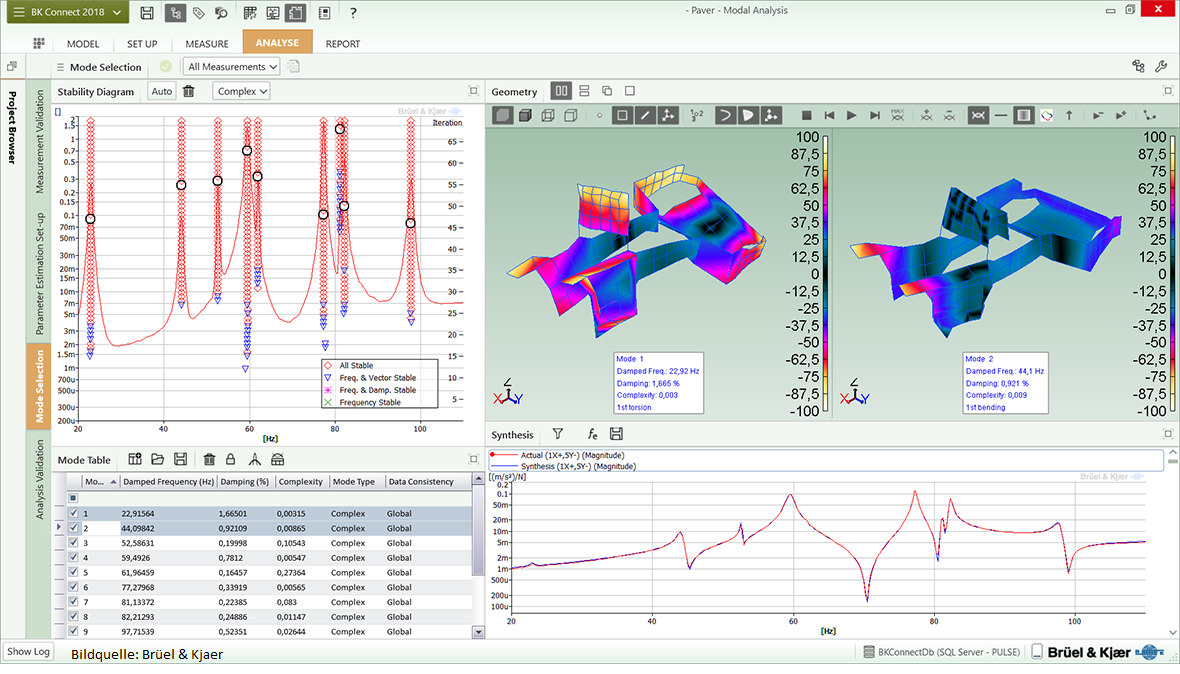
In most cases, noise and vibration problems arise from resonance phenomena due to operating forces like revolution speed or cutting forces. Vibration modes (natural frequencies) that are within the frequency range of the dynamic operating forces are potentially problematic. In the machining process, it is very difficult to identify the "oscillating" component (or assembly) without a measuring device.
Byhelp of modal analysis, the natural frequenciesof the machine are measured and the real dynamic machine behavior is displayed on the graphically animated model. Based on the measured data we determine the cause and support you with solution concepts up to implementation.

In most cases, noise and vibration problems arise from resonance phenomena due to operating forces like revolution speed or cutting forces. Vibration modes (natural frequencies) that are within the frequency range of the dynamic operating forces are potentially problematic. In the machining process, it is very difficult to identify the "oscillating" component (or assembly) without a measuring device.
Byhelp of modal analysis, the natural frequenciesof the machine are measured and the real dynamic machine behavior is displayed on the graphically animated model. Based on the measured data we determine the cause and support you with solution concepts up to implementation.
In most cases, noise and vibration problems arise from resonance phenomena due to operating forces like revolution speed or cutting forces. Vibration modes (natural frequencies) that are within the frequency range of the dynamic operating forces are potentially problematic. In the machining process, it is very difficult to identify the "oscillating" component (or assembly) without a measuring device.
Byhelp of modal analysis, the natural frequenciesof the machine are measured and the real dynamic machine behavior is displayed on the graphically animated model. Based on the measured data we determine the cause and support you with solution concepts up to implementation.
Are you looking for ways to make the production of your plant more reliable and profitable? With virtual commissioning, there is no conflict between reducing throughput time and increasing software quality. We can support you.
Based on many years of experience in the machine tool industry, we deliver custom-made software solutions including implementation and commissioning - all in one hand.